Angioplasty balloons
Overview
Angioplasty balloons are essential tools in the treatment of arterial blockages. These balloons, with their controlled inflation capability, reopen blocked arteries and help restore blood flow. Their design is optimized for use in sensitive and precise surgical procedures.
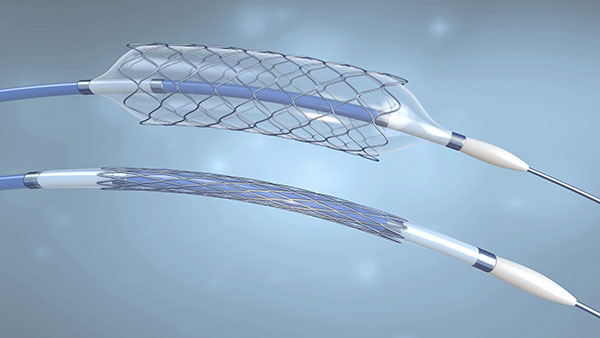
Components of Angioplasty Balloons
Angioplasty balloons consist of the following parts:
- Thin polymer tube: Designed to access the site of arterial blockage.
- Expandable balloon: Used to clear the blockage and reopen the artery.
- Side port: Enables the injection of contrast agents and pressure regulation.
Placement Procedure for Angioplasty Balloons
The balloon is guided through the artery to the site of the blockage. Once in place, it is inflated using an inflator device to clear the obstruction. After deflation, the balloon is carefully removed from the artery.
Applications of Angioplasty Balloons
Angioplasty balloons are used in the following treatments:
- Reopening blockages in coronary arteries.
- Clearing obstructions in saphenous vein bypass grafts.
- Treating blockages in peripheral or renal arteries.
Types of Angioplasty Balloons
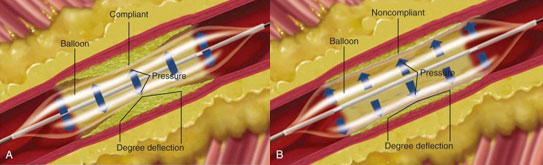
Two main types of angioplasty balloons, Non-Compliance (NC) and Semi-Compliance (SC), are widely used. The primary distinction between them lies in their compliance (adaptability). NC balloons expand uniformly and are better suited for harder areas, whereas SC balloons are more adaptable and perform better in softer regions.
- Non-Compliance (NC) Balloons
- Uniform expansion in all areas.
- Suitable for hardened sections with calcium deposits.
- Limited expansion to minimize uneven growth.
- Semi-Compliance (SC) Balloons
- Greater expansion with increased pressure.
- Adaptable to areas with less resistance
- Suitable for regions requiring greater flexibility.
Conclusion
Angioplasty balloons, with their advanced design and reliable performance, are indispensable tools in the treatment of arterial blockages. Choosing the appropriate type of balloon based on the patient’s condition and the characteristics of the blockage site plays a pivotal role in the success of the treatment.
- Hayes, D. L., Asirvatham, S. J., & Friedman, P. A. (Eds.). (2021). Cardiac pacing, defibrillation and resynchronization: a clinical approach. John Wiley & Sons.
Products
Cardiovascular
Orthopedics
Dentistry

