Angioplasty guidewires
Overview
Guidewires are advanced medical tools specifically designed to facilitate angioplasty procedures and open blocked arteries. These devices play a critical role in clearing arterial obstructions and restoring normal blood flow. Angioplasty is a medical procedure similar to angiography, in which a specialized wire is used to resolve arterial blockages. During the process, the guidewire is inserted into the artery through its entry point, and its movements are entirely controlled externally. By maneuvering the wire through narrowed sections of the artery, it effectively removes obstructions and allows blood vessels to regain their normal function.
Features and Components of Guidewires Guidewires are categorized based on their structure and components:
- Core Material:
- Nitinol: Provides high flexibility, resistance to twisting, and the ability to retain its shape, but it has limited formability.
- Stainless Steel: Offers precision and is ideal for accessing lesion sites. A combination of both materials is often employed, such as using a stainless steel core for rigidity and a nitinol tip for enhanced flexibility.
- Core Diameter: Common sizes include 0.014, 0.018, and 0.035 inches.
- Tip Design: The distance between the core and the tip, as well as the gradient of tapering, is crucial for accessing arterial branches.
- Distal Section: The spring coil in this section provides additional flexibility to the guidewire tip, but it increases friction. A polymer coating is applied over the spring coil to minimize friction and enable smoother navigation.
- Surface Coating:
- Hydrophilic Coating: Reduces resistance, allowing the guidewire to move smoothly through arteries; however, it decreases tactile feedback.
- Hydrophobic Coating: Materials such as PTFE or silicone enhance control and preserve tactile sensation, striking a balance between ease of movement and feedback.
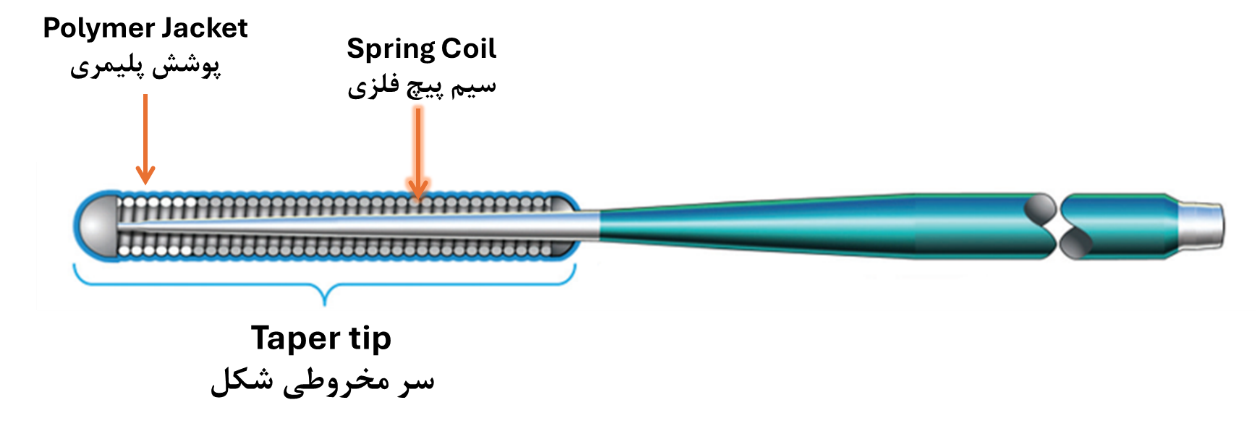
Common Types of Guidewires
- Workhorse Guidewires:
- Designed for accessing partially or fully blocked arteries.
- Features a flexible and shapeable tip for seamless movement within blood vessels.
- Specialty Guidewires:
- Engineered for navigating fully obstructed arteries.
- Equipped with a sturdier tip capable of exerting greater pressure, making them suitable for breaking through hard deposits inside vessels.
- Urological Guidewires:
- Used in urological procedures with fewer design complexities compared to angioplasty guidewires.
- As they do not pass through arteries, they are classified as lower-risk devices.
Conclusion
Guidewires are advanced tools designed to facilitate angioplasty by clearing arterial blockages and restoring natural blood flow. These devices are categorized based on core material, tip design, and coating, and they play an essential role in treating partial and complete blockages, as well as in urological applications.
- Tummala S, Patel M. Basics of Guidewire Technology and Peripheral Artery Disease. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2023 Jun 16;40(2):129-135. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-57258. PMID: 37333742; PMCID: PMC10275669.
Products
Cardiovascular
Orthopedics
Dentistry

